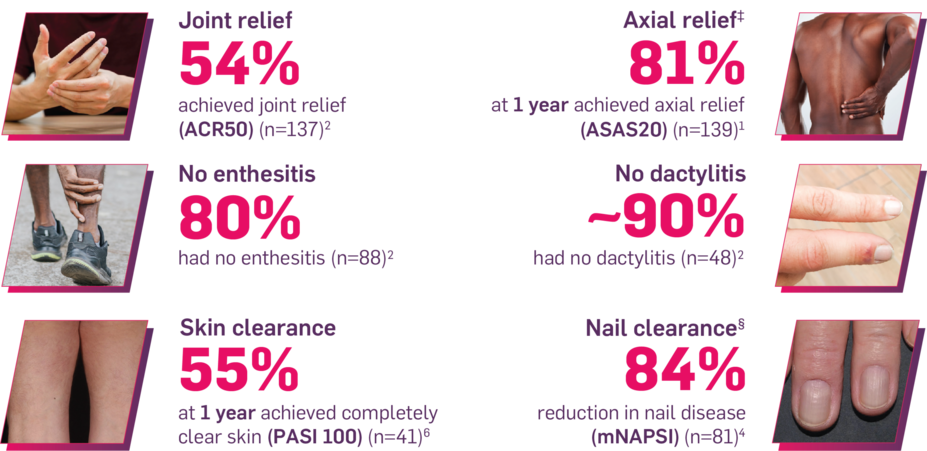
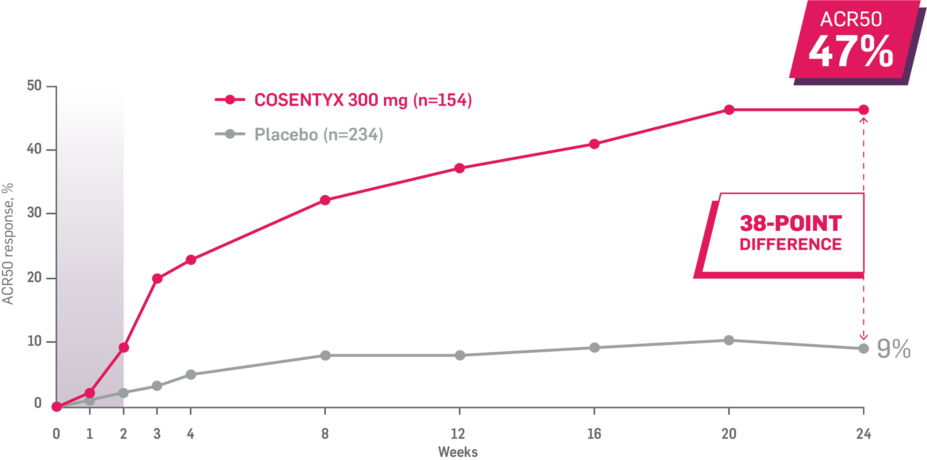
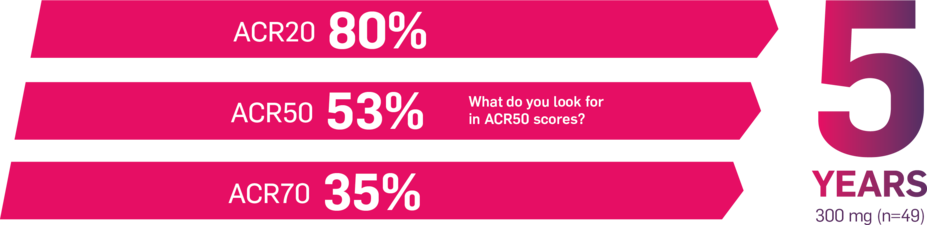
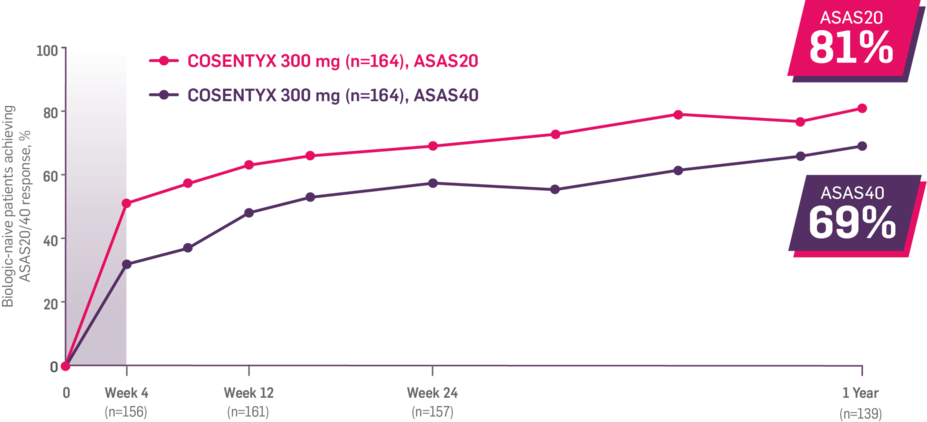
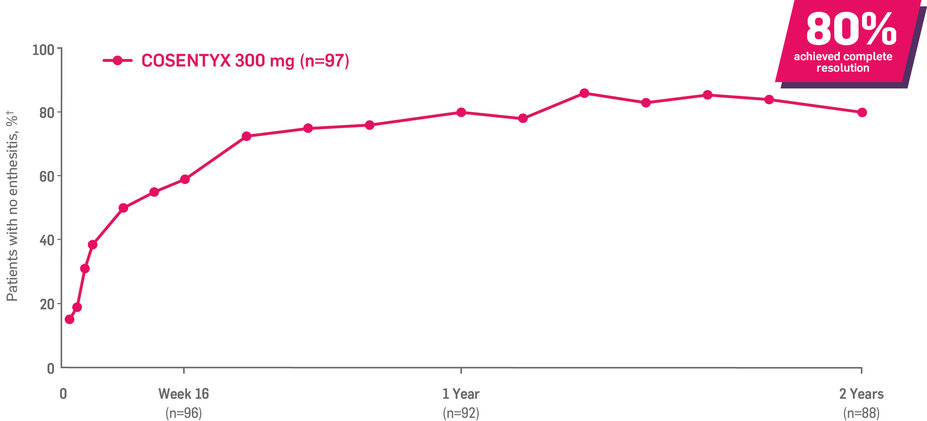
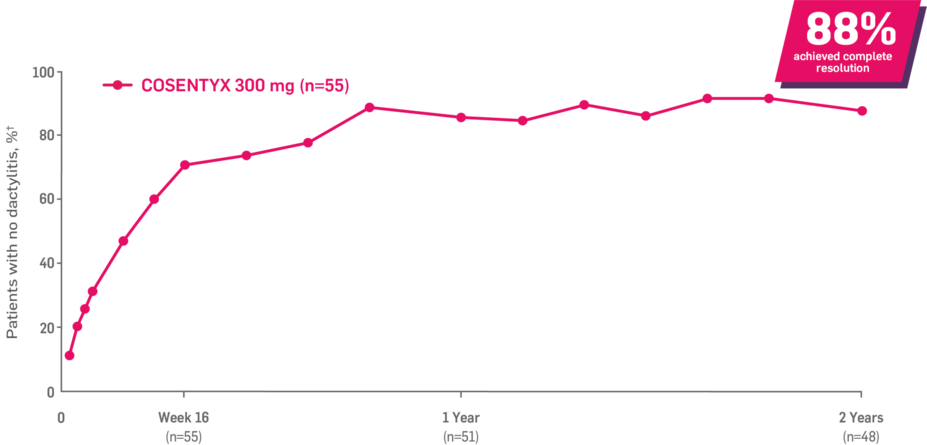
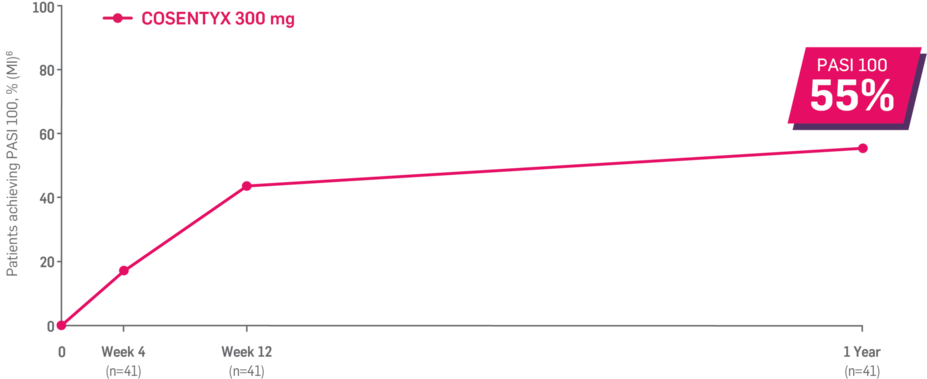
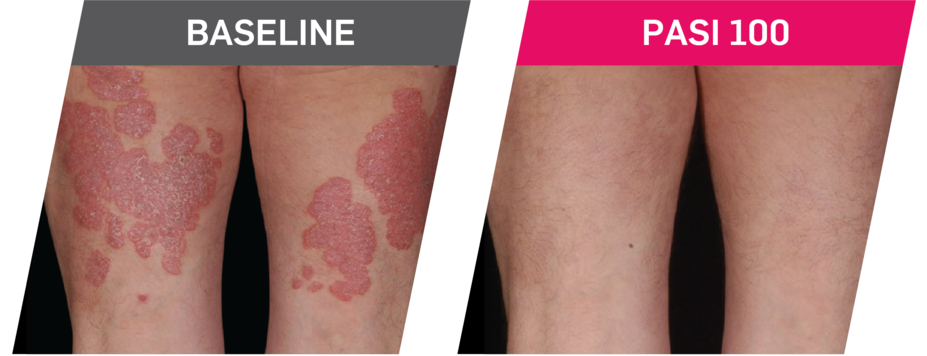
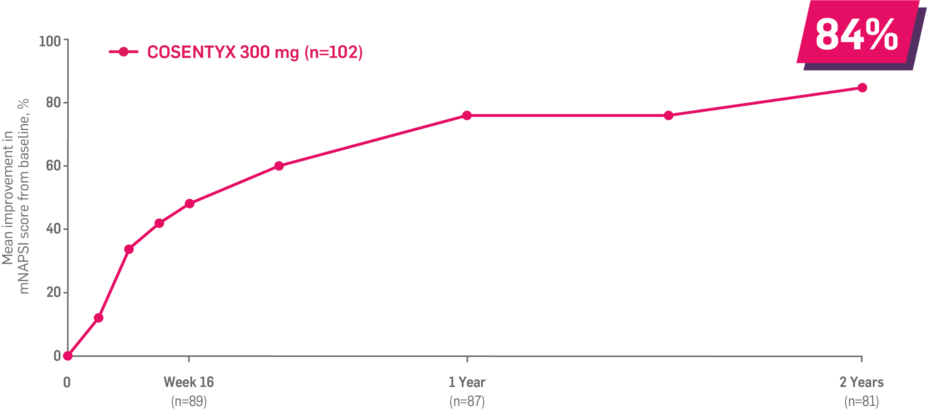
Results up to 2 years, as observed in patients on 300 mg
150 mg across manifestations up to 2 years: ACR50: 60% (n=132); ASAS20: 80% at 1 year (n=141); enthesitis: 82% (n=85); dactylitis: 86% (n=43); mNAPSI: 89% (n=78).1-4
In FUTURE 5,* ACR50, dactylitis, enthesitis, and mNAPSI were prespecified exploratory end points at 2 years in biologic-naive patients. In MAXIMISE,* ASAS20 at 1 year was a prespecified exploratory end point. In MATURE,* a study of patients with PsO, PASI 100 at 1 year was a prespecified exploratory end point in a mixed population. No clinical or statistical conclusions can be drawn.1-4,6,7
*All trials used SC administration.
†The effectiveness and safety of COSENTYX IV formulation are based on the pharmacokinetic exposure and extrapolation of the established effectiveness and safety of SC COSENTYX in adult patients with active PsA, AS, or nr-axSpA.5
‡Data from the MAXIMISE trial, whose study design, patient population, and dosing regimen are consistent with those of FUTURE 2. In FUTURE 2, 20% of patients had spondylitis with peripheral arthritis. MAXIMISE primary end point: 63% experienced relief on COSENTYX 300 mg at Week 12 vs 31% with placebo, as measured by ASAS20 (P<0.0001) (n=164) (MI).1,5
§Nail data in PsA were consistent with those in the dedicated nail PsO study, TRANSFIGURE. Improvement from baseline NAPSI at Week 16 (primary end point) (MMRM) was 46.1% for COSENTYX 300 mg (n=63) and 11.7% for placebo (n=56) (P<0.0001).15
Definitions
ACR, American College of Rheumatology; AS, ankylosing spondylitis; ASAS, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society criteria; IV, intravenous; MI, multiple imputation; MMRM, mixed model for repeated measures; mNAPSI, modified Nail Psoriasis Severity Index; NAPSI, Nail Psoriasis Severity Index; nr-axSpA, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, plaque psoriasis; SC, subcutaneous.
References
1. Baraliakos X, Gossec L, Pournara E, et al. Secukinumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis and axial manifestations: results from the double-blind, randomised, phase 3 MAXIMISE trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(5):582-590.
2. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; May 2019.
3. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report. PASI 90 and ACR Components data. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; January 2020.
4. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5):
2-Year Interim Report. mNAPSI and PASI 100 data. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; October 2019.
5. Cosentyx. Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.
6. Sigurgeirsson B, Browning J, Tyring S, et al. Secukinumab demonstrates efficacy, safety, and tolerability upon administration by 2 ml autoinjector in adult patients with plaque psoriasis: 52-week results from MATURE, a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35(3):e15285. doi:10.1111/dth.15285
7. Data on file. CAIN457A2325 (MATURE): Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; August 2020.
8. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): Clinical Study Report. Interim Analysis-Week 24. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; November 2017.
9. Data on file. CAIN457F2312 (FUTURE 2): 5-Year Interim Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; May 2019.
10. Data on file. CAIN457F2312 (FUTURE 2): Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; October 2014.
11. Data on file. CAIN457F3302 (MAXIMISE): 1-Year Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; August 2020.
12. Mease P, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al. Secukinumab improves active psoriatic arthritis symptoms and inhibits radiographic progression: primary results from the randomised, double-blind, phase III FUTURE 5 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(6):890-897.
13. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report. PASI 100 data in biologic-naive patients. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; April 2020.
14. Coates LC, Soriano ER, Corp N, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(8):465-479.
15. Data on file. CAIN457A2313 (TRANSFIGURE): Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; November 2015.
16. Pasch MC. Nail psoriasis: a review of treatment options. Drugs. 2016;76(6):675-705.
17. Gossec L, Kerschbaumer A, Ferreira RJO, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(6):706-719.
18. Data on file. CAIN457A2313 (TRANSFIGURE): Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; October 2017.
19. Data on file. CAIN457F2312 (FUTURE 2): Interim Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; November 2015.
20. Data on file. CAIN457F3302 (MAXIMISE): Data Analysis Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; June 2016.